Loading screen: bootstrap process
When accessing a Notebook link, you land on a loading page, this is called the bootstrap phase.
During that phase, the following steps will occur:
- Retrieve the project/repository content
- Locate the environment definition and/or its lock file
- Check for a cached environment:
- If found, redirect to the JupyterLite page
- If not found, proceed to environment resolution
- Resolve the environment (if no lock file is provided)
- Upon successful resolution, redirect to the JupyterLite UI with your environment ready for use
warning
If the resolution of the environment fails, you will see solver issues, helping you to debug your environment definition. See the Environment creation documentation for guidance on how to make an environment that is compatible with Notebook.link.
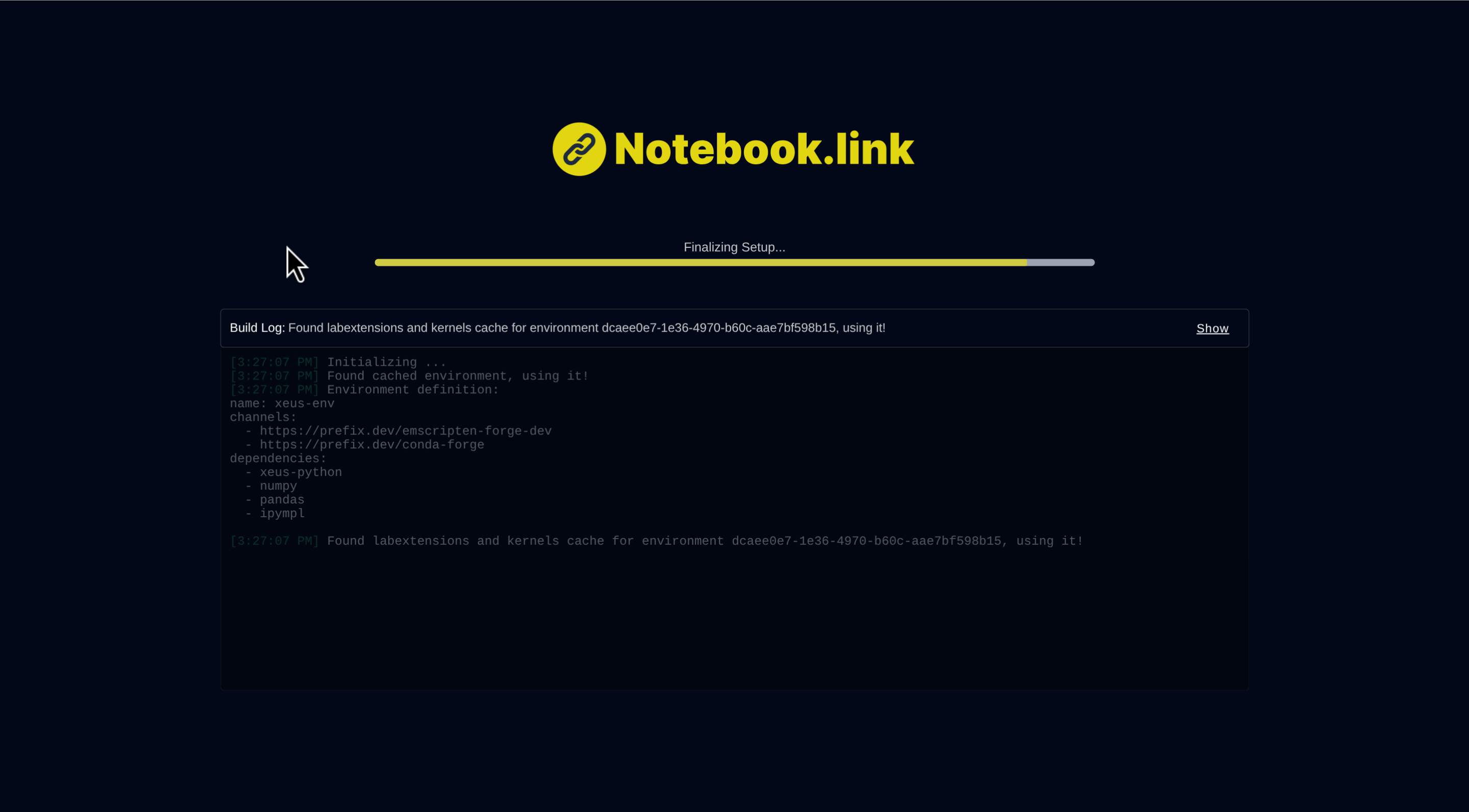
The loading screen contains a log window, helping you see what happens during the bootstrap phase. You can view the detailed log by clicking the Show button.
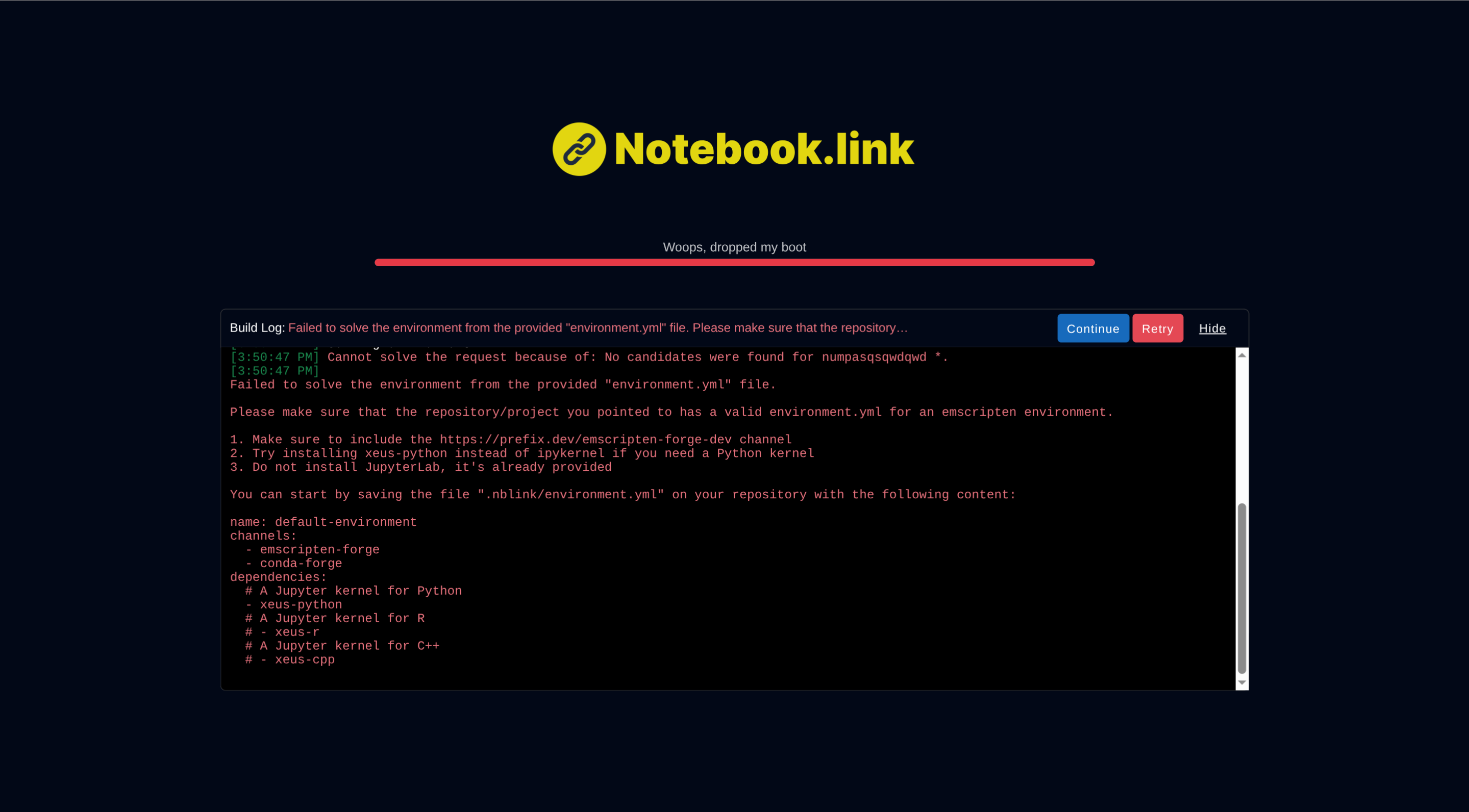
note
If an error occurs during bootstrapping, you have two options:
Continue: continue with the default environment (only contains a Python kernel). e.g. This can be useful if you don't have rights to modify theenvironment.ymlin the Github repository you link to. Note you will still be able to install required packages to run the notebooks, but dynamically installing new packages.Continue:
- Proceed with the default environment (contains only a Python kernel)
- Useful when you lack permissions to modify the repository's
environment.ymlfile - You can still install required packages dynamically
Retry:
- Reset your browser cache and restart the bootstrap process
- Helpful when invalid cached data prevents successful bootstrapping :::